Among the thousands of fishes Americans catch or eat, striped bass or stripers hold a unique position. Whether fried, boiled, or grilled, the firm, flaky meat of striped bass is one of the best gifts from the ocean. Bon appétit! But despite their great taste and nutritional value, there are question marks over whether or not they are safe to eat.
According to different fish consumption advisories, striped bass is not safe for children, nursing or pregnant women, and women of childbearing age to eat. Striped bass may contain chemical pollutants that can cause serious health problems. Every other person is restricted to 2 servings per week.
The rest of this article will comprehensively discuss everything about eating striped bass, including who can and shouldn’t eat them. How much you can and how often you should eat them, potential risks of chemicals in striped bass, and how to properly prepare stripers before eating them.
Can You Eat Striped Bass?
All fish contain some amount of pollutants. However, sport and predatory fish, such as striped bass, can accumulate chemicals and heavy metals in their bodies to a level where they are harmful when eaten.
The group of people at greater risk are children between the ages of 1 and 17 and women aged 18 to 45.
If you’re in this group, you must avoid eating striped bass as much as possible, as you are more vulnerable to damage from the contaminants in it (OEHHA).
How Much Striped Bass Can You Eat?
If you’re not in the high-risk group, you can still eat striped bass but only in moderation of 4 servings a month or two servings a week.
You may also need to check for fish advisories in your state to find guidance and information on the amount of fish you should eat.
It is important to note that a serving is different from a full meal. Typically, the recommended serving is 3.5 ounces (99 grams) of fish. As a rough estimate, use the size and thickness of your hand.
Consider spacing your meals and not eating the recommended servings all in one go.
This advice for everyone else in the low-risk group is to help ensure there is a lower risk of cancer and liver and kidney damage.
What Happens if You Eat Contaminated Striped Bass?
The two major causes of concern are mercury  and polychlorinated biphenyl (PCBs) in striped bass. These two chemicals are incredibly dangerous.
and polychlorinated biphenyl (PCBs) in striped bass. These two chemicals are incredibly dangerous.
If you’re in the high-risk group and consume them in high amounts, you can suffer from severe health problems such as congenital disabilities, liver and kidney damage, and cancer (Environmental Defense Fund).
According to the EDF, mercury primarily acts as a neurotoxin when consumed and impairs development in the central nervous system.
In developing fetuses, babies, and young children, it can cause irreversible brain damage and learning disabilities since their brains are not yet fully developed.
Women of childbearing age who are exposed to high amounts of mercury before becoming pregnant may give birth to children with the impaired development and slow learning abilities.
Also, nursing mothers with mercury in their system can pass it on to their infants through breast milk.
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are very toxic chemicals that can cause cancer, reproductive diseases, and nervous system disorders.
Fetuses and babies are also the most vulnerable to PCB damage as prolonged exposure can cause developmental and neurological problems (Mayo Clinic).
PCBs accumulate in the fatty tissues of fishes and have a half-life of 10 to 15 years. This half-life means that if you consume a striped bass that contains PCBs, half of the PCBs can stay in your body for up to 15 years (NYS Department of Health).
How Do Mercury and PCBs Get Into Striped Bass?

Striped bass accumulates contaminants like mercury and PCBs in a variety of ways. Chemicals on land or air can be transported into streams and rivers by rain.
Also, stormwater runoff and industrial discharges can deposit harmful chemicals into the water where they are taken up by fishes.
For example, mercury is first released into the air by volcanoes, forest trees, weathering of rocks, and human activities such as coal burning and mining operations.
It then settles onto the land, and rain and surface water runoff wash it into water bodies. When it gets into water, mercury is converted into methylmercury by bacteria and other microorganisms.
Fishes, especially bottom dwellers like striped bass, then absorb methylmercury from their food and through their gills as they swim across the water. The level of contamination usually depends on the river and its location.
When fishes consume methylmercury, it bonds tightly to the protein in their muscles and builds up over time. If you eat this type of fish, the chemical will also accumulate in your tissues and organs (Department of Environmental Conservation).
Striped bass can also absorb PCB from the water and their food.
PCBs were once used for a variety of industrial applications, including hydraulic fluid, lubricants, and electrical transformers and capacitors.
Their use was later banned in the United States in 1979.
Unfortunately, PCBs persist in the environment due to their heavy past usage. Just like mercury, PCBs accumulate in the organs and fatty tissues of fish. They settle into seabed and lake bottoms and get consumed by fishes.
How Much Mercury Does Striped Bass Contain?
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the maximum safe dose of mercury is 0.46 µg/g or ppm per week for a person weighing 75 kilograms (165 pounds). This value is known as the reference dose and can be in a single serving or an accumulation of 3 servings in a week.
Now, the average mercury concentration in striped bass is 0.17 µg/g or ppm (FDA). This means that if you consume two servings of striped bass per week, you’ll still be within the recommended dose. If you go above two servings, you’ll be getting a mercury concentration that’s greater than the maximum safe dose.
Do Some Stripers Contain More Pollutants Than Others?
Yes, the amount of mercury and PCBs in different stripers vary with size, age, and the location where they are caught. All striped bass contain some mercury. As they forage and grow larger, more amounts of methylmercury accumulate in their tissues and fats.

Typically, an older or larger striped bass will have more mercury than a smaller one (Wikipedia).
For example, a 30 inch (76 cm) striped bass, which is about seven years old, will have a lower concentration of mercury and PCBs than a 40 inch (102 cm) striped bass that has been accumulating these contaminants for 13 years.
When a bigger fish eats a smaller fish that has mercury or PCBs, it’s level of contaminants biomagnifies. This process is known as biomagnification. So, the longer the fish lives, and the longer it stays in contaminated waters, the greater its mercury and PCBs concentration.
Also, farmed striped bass may contain fewer toxins than wild striped bass. Another consideration is the region where the fish is caught.
For example, in the United States, waters, such as the Hudson River and the Long Island in New York, may contain higher levels of mercury and PCBs than other rivers in the East Coast Rivers (NYS Department of Health).
Because of the varying levels of mercury and PCBs in different fishes in different regions, the EPA advises checking local advisories for information and guidelines on safe fish consumption in your area.
How to Properly Prepare Striped Bass
Proper cleaning and cooking can help make a difference in the number of chemical pollutants you consume in striped bass.
Although mercury accumulates in the tissue of fish and no method of cleaning or cooking can reduce its concentration, exposure to toxins such as PCBs and dioxin can still be reduced through proper skinning, trimming, and cooking.
Immediately after catching your fish, put it in a splash well and let it bleed it out. If you’re not ready to cook it immediately, put it in a cooler with ice.
Check this beginners guide on how to catch striped bass from the surf.
However, don’t wait too long before cleaning and gutting it. The EPA recommends removing the skin, fat, and internal organs as these are the places where toxins are likely to accumulate.
Here are other tips and precautions from the EPA:
- Cut and throw away the head of the fish. Fish liver, guts, and kidneys should also be thrown away.
- Fillet the fish properly and remove its skin before cooking it.
- Trim away the fat along the sides of the fish, across the belly flap, and along its top back.
- Cook the skinned and trimmed fish on a rack to allow all the fat to drip away.
- Avoid using the dripping from the fish to prepare the sauce or to flavor the meal as they may contain a higher level of toxins.
- Reduce or avoid frying or deep-frying fish as frying seals in harmful chemicals that may be present in the fat of muscle tissue.
- If you prefer smoking your striped bass, it is a good idea to fillet the fish and trim off its skin before smoking.
During cleaning, be careful not to cut into the stomach or any part of the intestine as it can release stomach acid and contaminate the meat. If this happens and the meat becomes contaminated, wash it thoroughly with cold water.
After you’re done skinning, trimming, and cleaning, clean the table and area immediately. Collect the head, kidneys, liver, and guts and dispose of them.
If you can’t throw them away immediately, double bag and freeze them until you get the chance to dispose of them, another way to get rid of the guts is to use them as bait for another catch.
When cooking striped bass or any other fish, ensure that the core of the meat reaches a temperature of 145°F (62°C) to prevent food-borne illness.
If you don’t have a meat thermometer to check the temperature, use a fork to easily check if the meat separates. The meat should also be clear and opaque.
How to Properly Store Striped Bass

 fillet in packing on ice sell in supermarket. Food image.
fillet in packing on ice sell in supermarket. Food image.Striped bass, just like every other fish, must be stored properly to keep it from spoiling, and to preserve its flavor and quality. The key is storing the fish at a controlled temperature.
Between the time you catch or buy striped bass and eat it, there are several methods by which you can keep it fresh.
Put the Striper on Ice
Fish can rot quickly, so it is important to keep it as cold as possible. Place your catch in a cooler and pour ice on it. It’s best to use shaved ice and an insulated cooler with a drain plug.
Just add a little water and plenty of ice. Leave the drain plug open so that the ice water can drain out, and new ice can be added.
If you’re using a cooler without a drain plug, regularly pour out the melted ice water and replace the ice. Keep the stomach and gill areas fully surrounded with ice.
If you’re storing more than one fish, ensure that they don’t touch each other in the cooler.
Storing your striped bass with this method will keep it good for up to 2 days. However, it is best to clean it within 24 hours of catching or buying it.
with this method will keep it good for up to 2 days. However, it is best to clean it within 24 hours of catching or buying it.
Store It in the Refrigerator
When stored in the refrigerator, striped bass can last up to 3 to 4 days (Isolator Fitness). Before placing the fish in the fridge, rinse it thoroughly in cold water and use a clean cloth or a paper towel to pat it dry.
To prevent exposure to air, wrap it in an aluminum foil or a plastic wrap.
You may also put the fish on ice in the refrigerator. Ensure it is wrapped in a container so that it doesn’t touch the ice directly or sit in it. Another option is to have your fish in a cooler and then placing it in the refrigerator.
For pieces of meat, wrap them tightly in an aluminum foil before putting them in the cooler. Remember to regularly drain out the melted ice water and replace the ice.
Cooked leftover striper should be stored in a shallow covered container before placing it in the refrigerator. Leftovers can last up to 2 to 3 days in the fridge. Ensure that the refrigerator is at or below 40°F (4°C).
Keep Striped Bass in the Freezer
If you won’t be using your fish within 2 to 3 days, it’s best to store it in the freezer. Frozen fish can last up to 9 months when stored at 0°F (-18°C) or lower.
when stored at 0°F (-18°C) or lower.
However, it is best consumed after 2 to 3 months. Be sure to rinse the fish thoroughly before freezing it. Wrap the cleaned pieces in a freezer-safe bag such as a Ziploc bag and press out all the air from it.
You may also wrap individual pieces in aluminum foils and place them in the freezer. This can help you in sticking to the recommended weekly servings.
It also helps to save freezer storage space, and you can easily thaw the pieces when you’re ready to eat them.
How to Tell if Striped Bass Has Gone Bad
Fish, in general, can go bad if something goes wrong with your storage method. You can tell whether your striped bass is still safe to eat by checking its appearance and texture.
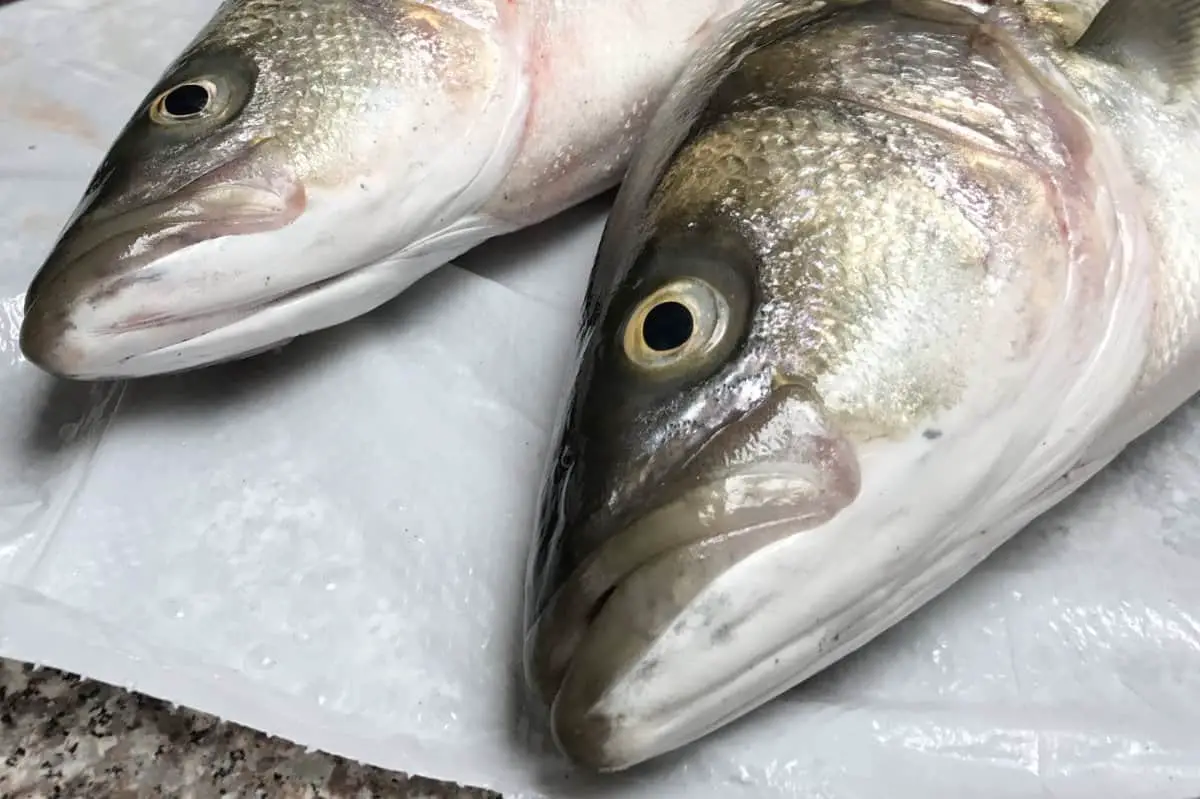

If it has spots or discoloration, it’s best to discard it. It’s also not worth eating fish that has a slimy texture or feels slippery to the touch.
The eyes of the fish should be clear and shiny, rather than cloudy or sunken. Also, if you check for a pungent or rancid smell, your striper should smell like fish instead of ammonia.
Here are some additional safety and storage tips:
- Do not thaw food in the microwave as some parts of the meat may cook during thawing. Instead, thaw it in a refrigerator or with cold water.
- Do not place thawed fish back in the freezer.
- Avoid keeping cooked fish at room temperature for more than 2 hours or 1 hour if the temperature is above 90°F (32°C).
Conclusion
Striped bass can be part of a healthy diet because of its taste and nutritional benefits. However, it can contain mercury, PCBs, and other chemical pollutants.
For this reason, it is recommended that children, pregnant women, nursing mothers, and women of childbearing age avoid eating striped bass.
Every other person outside this group can safely eat striped bass but only two servings per week. The following tips can help you reduce your exposure to harmful pollutants in striped bass:
- Throw away the head, liver, guts, and kidneys of the fish.
- Remove its skin and allow all the fat to drip away.
- Trim away fat along its back, belly, and sides.
- Avoid frying or deep-frying your striper.
- Throw the fish if it shows any signs of spoiling.

